- Gene Technology: The era of gene
technology began in the 1970s with the development
of several methodologies such as the use of
restriction enzymes (restriction
endonucleases), in vivo gene cloning, and DNA
sequencing.
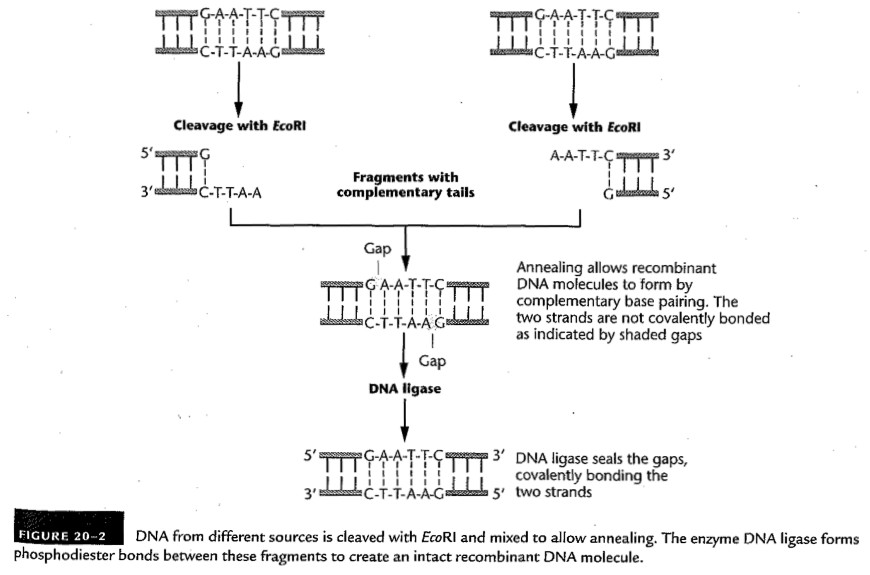
- Restriction Enzymes: These
endonucleases recognize a certain palindromic DNA
sequences and cut the molecule there.
|
|
- Gel Electrophoresis: This
technique can be used to separate DNA molecules
according to size. (Know: Southern blot, Northern
blot, Western blot -- pp. 560-561)
|

|
- Shotgun and Other Cloning Methodologies:
Early gene cloning experiments were done using
restriction enzymes to ligate target DNA to vector
DNA. This hybrid molecule was then used to
transform E.
coli. Cloning procedure like this
can be used to build genomic libraries or cDNA
libraries. However, mRNA is isolated and reverse
transcriptase is used in building cDNA libraries.
|
|
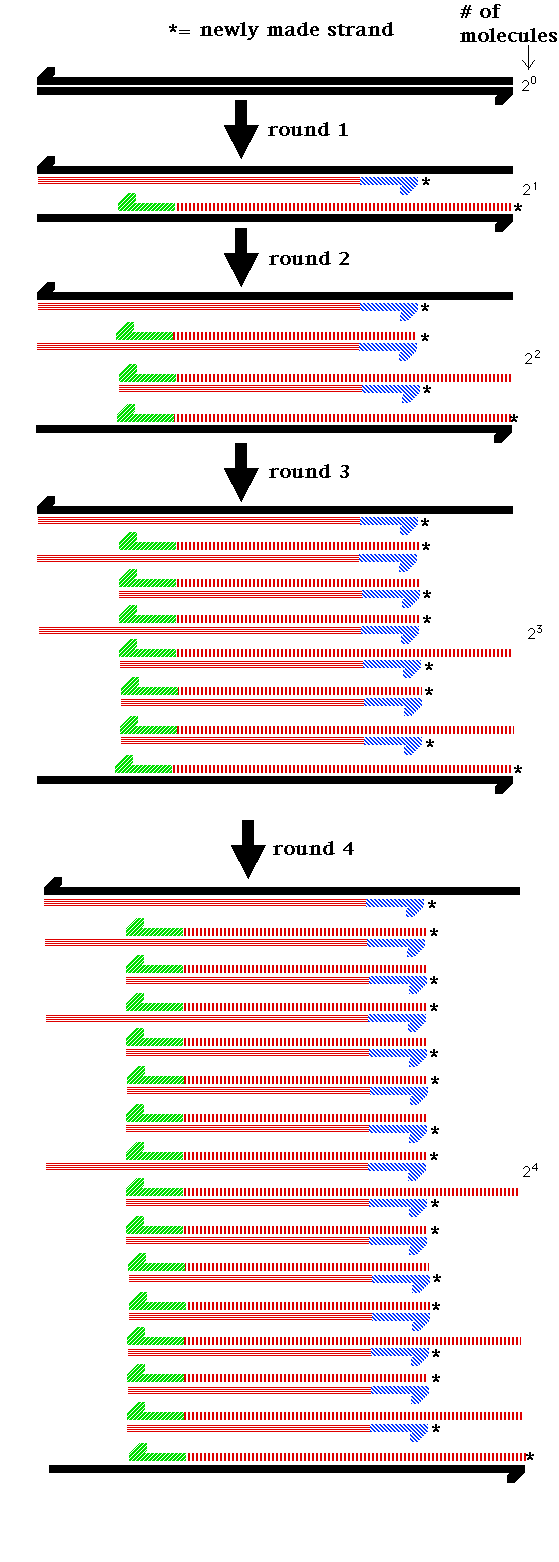
- PCR: This in vitro methodology
amplifies a segment of DNA 230
fold.
|
 |
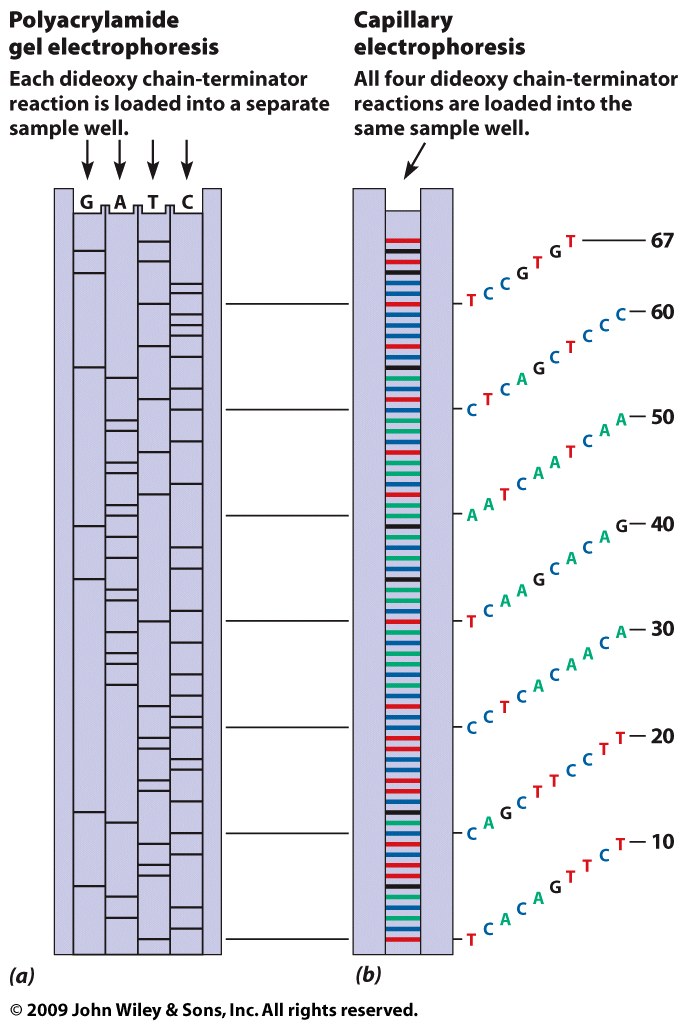
- DNA Sequencing: Early sequencing
methods used radioactive labels. The late 20th
century's technology was Sanger sequencing. The
technology of uses the dideoxy method.
"Next-Generation Sequencing" is quickly becoming
more affordable and is replacing Sanger
sequencing. Some of these methodologies include
Pyro Sequencing and HiSeq/miSeq.
|
 |
- The Human Genome Project: The
mega-sequencing project undertaken at the end of
last century had as its goal the sequencing of the
3 billion base-pair human genome. (What are SNPs?)
|
|
- Microarrays (Gene Chips): One of
the many methodologies used in genomics is the
microarray. With this technique, it is possible to
ask questions like, "What genes are expressed in
cancer cells that are not expressed in normal
cells."
- Next-Generation DNA Sequencing:
New rapid, cheaper sequencing methodologies make
possible the routine whole genome sequencing. This
opens the door to detailed investigation of the
role of all genes in determining trait (like
disease conditions).
- CRISPR: What is it? (Be able to
answer this question on the next test.) See this
link and this
link and this
link.
|
 |