DNA's role as
the genetic material includes 1) carrying information (in its
base sequence), 2) copying that information (replication), and
3) giving meaning to that information (determining traits). DNA
does this last job by determining what proteins (including
enzymes) are made in the cell. Protein synthesis involves RNA
synthesis (transcription) and polypeptide synthesis
(translation). Crick proposed that his information transfer was
one way (The central dogma of genetics).
|
 |
- Genes and Polypeptides: Proteins are made up
of one or more polypeptides, which are chains of amino acids
joined by peptide bonds. A gene can be defined as the
DNA coding for one polypeptide ("One gene, one
polypeptide"). Yanofsky
demonstrated colinearity of the gene and polypeptide.
|
- Transcription:
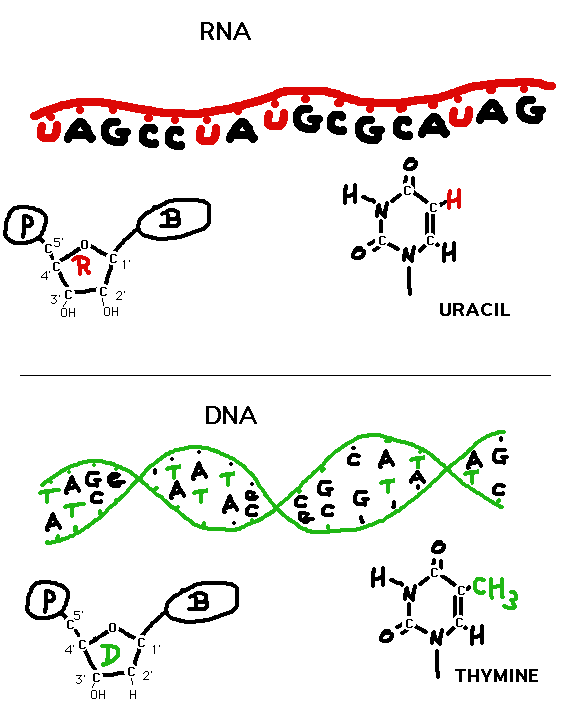
Transcription is DNA-directed RNA synthesis. The sequence of
a segment of a DNA molecule determines the sequence of an
RNA molecule. RNA is very similar to DNA in structure, but
is usually shorter, is usually single stranded, has ribose
in place of 2'-deoxyribose, and has uracil in place of
thymine (uracil base pairs with adenine just like thymine
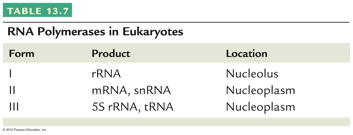
does). Transcription is the process of making mRNA,
ribosomal RNA (rRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), as well as other
small RNAs.
|
 |
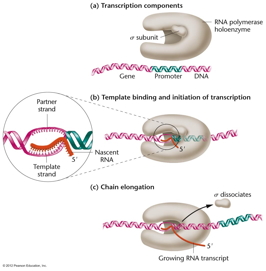
- RNA
Polymerase: The enzyme that transcribes
DNA is called RNA polymerase. RNA polymerase uses the
nucleoside triphosphates (ATP, GTP, CTP, UTP) and RNA
polymerization occurs just like DNA polymerization does.
That is, it begins with the 5' end and the new RNA
molecule grows in the 5' to 3' direction (a nucleotide is
added to the 3'-OH). RNA polymerase uses one strand of the
DNA molecule as the template strand with the 4 bases of
DNA (A, G, C, T) specifying which RNA nucleotides will be
added (U is added when the template DNA nitrogen base is
A). As with DNA replication, the newly-made RNA molecule
is antiparallel to the template DNA. However, unlike DNA
polymerase, RNA polymerase does not need a primer but can
add start a new RNA molecule with a single NTP (therefore,
the first nucleotide of an RNA molecule has 3 phosphates
on its 5' end). Only one strand of the DNA double helix is
used as a template. That template strand is used is called
the template strand and the strand not used is the
non-template strand. An RNA molecule made by transcription
is called a transcript.
|
|
- Promoters
and Termination Sites: The site where
RNA polymerase binds and begins transcription is called
the promoter. Transcription stops at a termination site.
|
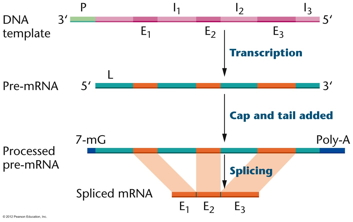
- RNA
Processing: In eukaryotes, pre-mRNA
molecules undergo considerable processing before leaving the
nucleus and directing translation. This includes the
addition of a cap at the 5' end, a poly-A tail, and
splicing: the removal of introns leaving in exons.
|
 |
Things I Learned
at the Movies:
Should you decide to defuse a bomb, don't worry which wire to
cut. You will always choose the right one.
|
 Home
Home


