| We have already
encountered one major exception to Mendel's concepts, namely
linkage, which is an exception to his Law of Independent
Assortment. The other major exception is the presence of genes in
the cytoplasm, primarily in mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Mendel's laws are all based on nuclear gene heredity--that is
meiosis (although he knew nothing about meiosis). Cytoplasmic
genes do not segregate to daughter cells according to meiosis, so
do not obey his laws. For that reason, the inheritance of these
cytoplasmic genes is often referred to as non-Mendelian genetics. |
|
Organelle Genetics: There are two
separate Genetic Systems involved in the production of
mitochondria and chloroplasts:
- The
Nuclear System: Most proteins found in
mitochondria and chloroplasts are coded for by nuclear genes,
made on cytoplasmic ribosomes, then transported into
mitochondria.
- The
Organelle System Some proteins in these organelles
are coded for by organelle DNA and made on organelle
ribosomes.
|
Organelle Genomes: Mitochondria and
chloroplasts have their own small DNA molecules that are usually
circular (except in some algae and protozoa) and are present in
multiple copies in each organelle.
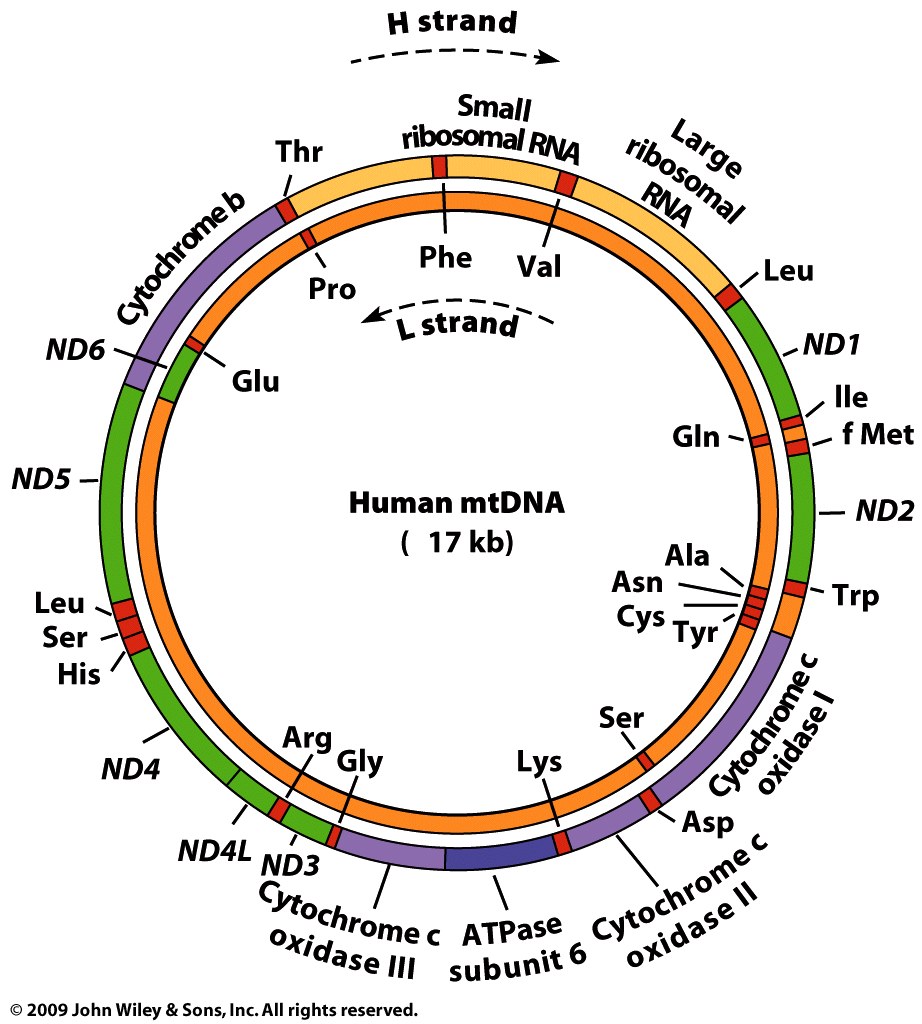
- Mitochondrial
DNA (mtDNA): Animal mtDNA molecules are usually
about 16-19 kb in size (about 1/100,000 of the nuclear genome,
altogether about 1% of cellular DNA). Plant mtDNA is 10 - 150
times larger than animal mtDNA (150 - 2500 kb). Since plant
mtDNA codes for about the same number of genes as animal mtDNA
and there is sometimes great variability in size even within
closely related plants, the excess may be "junk DNA." DNA
replication begins from the D-loop regions and replicates one
strand, then when reaching the D-loop again, the other strand
is replicated in the opposite direction. mtDNA codes for
tRNAs, rRNAs and a few proteins. There are two promoters on
the heavy strand, which has 28 genes including the two rRNA
genes, and one promoter on the light strand, which has 9
genes, 8 of which are tRNA genes. Transcripts are processed
into the appropriate RNAs. In vertebrate mitochondria "AGA"
and "AGG" are stop codons, but not "UGA", which codes for
tryptophan instead. "AUA" codes for isoleucine in most
organisms but for methionine in vertebrate mitochondrial mRNA.
mtDNA has a nucleotide substitution (mutation) rate that is
about 10 times higher than nuclear genomes, making mtDNA
comparisons useful taxonomically. Some mtDNA genomes have
introns. (..but, wait a minute..."For decades, scientists
thought they had a handle on the mitochondrial chromosome: 13
genes for proteins, two for rRNAs and 22 for tRNAs, all
tightly packed with no introns." ... but now
"it appears to contain small open reading frames that are hidden
inside the other genes.")
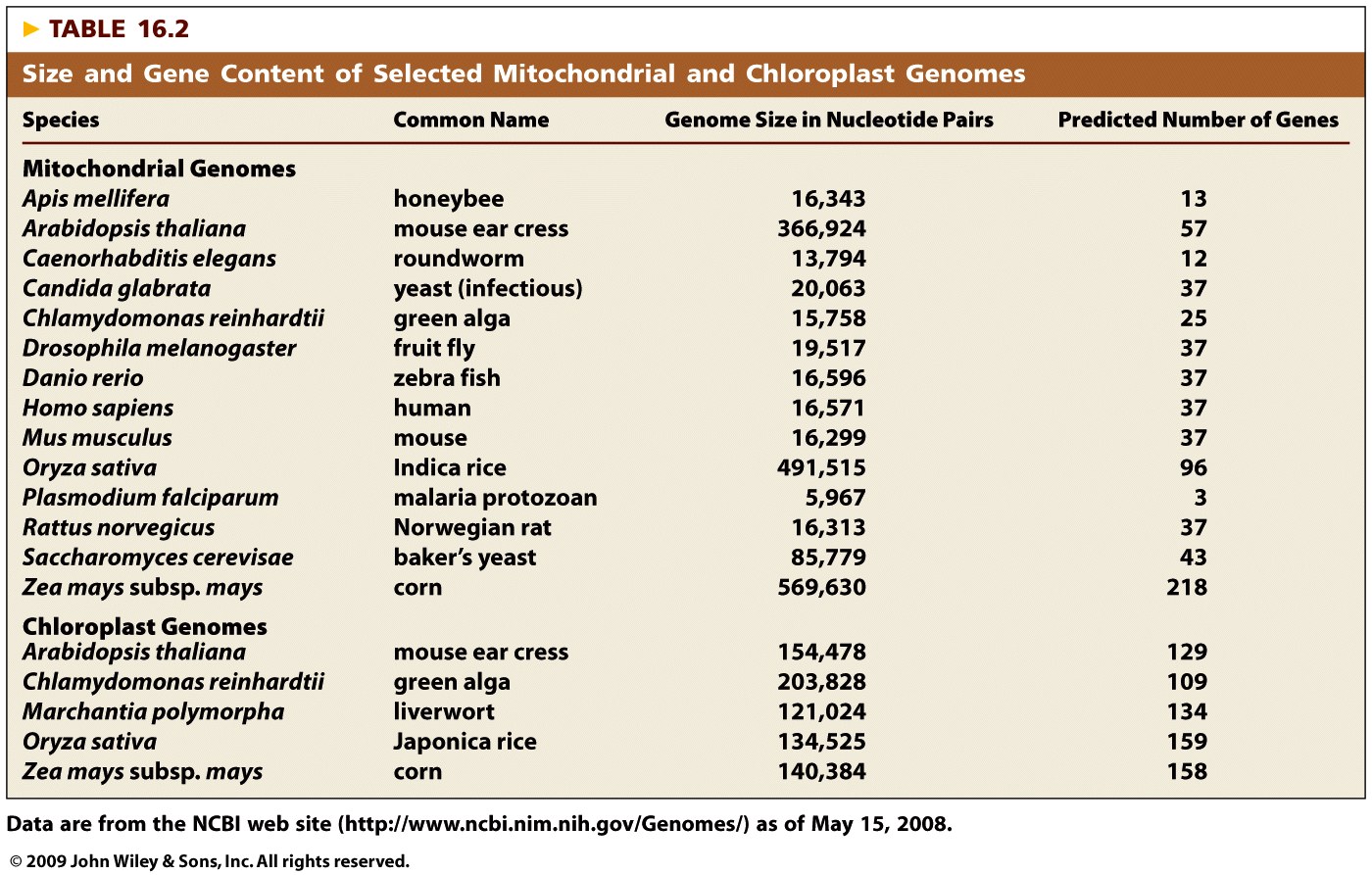
- Summary: Animal mtDNA is circular and usually about 16,000
- 19,000 bp long. The D-loop is the replication origin
region of this molecule. It has an unusual method of
replication. DNA replication begins from the D-loop regions
and replicates one strand, then when reaching the D-loop
again, the other strand is replicated in the opposite
direction.In humans, there are two strands, H and L, with
two promoter on the H strand and one on the L strand.
Therefore, three RNA are transcribed then cut into the
appropriate mRNAs, rRNAs, or tRNAs. The mtDNA includes 13
genes for proteins involved in oxidative phosphorylation, 2
rRNA genes, and 22 tRNA genes. Mitochondrial DNA uses a
genetic code which is slightly different from the nuclear
code. Most of the proteins needed to make a mitochondrion
are coded for by nuclear genes. These proteins are imported
into the mitochondria.
|
|
- Chloroplast DNA (ctDNA or cpDNA): Plant
chloroplast DNA molecules are about 120 - 180 kb in size.
Higher plant ctDNA codes for about 120 genes, including rRNAs,
30 tRNAs, several rProteins, an RNA polymerase subunit,
several respiration-related proteins, plus other 40 proteins.
ctDNA has introns.
- Summary: ctDNA is much larger than animal mtDNA and may be
circular or linear.
|

|
| Organelle
Division: Mitochondria and chloroplasts are never made de
novo, but always come from pre-existing organelles. DNA
replication occurs throughout the cell cycle. Organelle division
occurs by furrowing of the inner membrane with DNA molecules being
distributed between the daughter organelles. |
 |
Organellar Inheritance: Inheritance
of mitochondrial and chloroplast genes is non-Mendelian
(cytoplasmic inheritance, extranuclear inheritance). In yeast,
this leads to random segregation of traits. In higher organisms,
non-Mendelian inheritance is seen as maternal inheritance, since
mitochondria and chloroplast are usually inherited via the ovum
only. Heteroplasmy and lead to mosaicism. Why are mitochondria
only inherited from the mother?:
http://science.sciencemag.org/content/early/2016/06/22/science.aaf4777.abstract
- Summary: Mitochondrial and chloroplast trait are inherited
maternally, resulting in a unique pedigree.
|
| Other Extranuclear Genes:
Endosymbionts like kappa (killer) in Paramecium. |
| Human
Mitochondrial Traits Many are lethal and
only seen with heteroplasmy (some normal mitochondria present). |



